A novel carbon capture technology developed by The University of Texas at Austin speeds up the conversion of atmospheric CO2 into hydrates for ocean storage, offering a safer and more efficient alternative to underground reservoir injection. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Researchers have developed a new method for carbon storage that accelerates the formation of carbon dioxide hydrates using a chemical-free process.
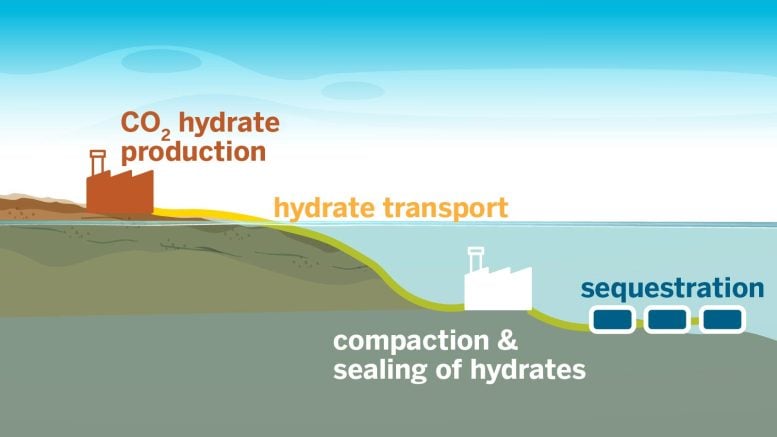
This technique, which converts CO2 into stable ice-like materials for ocean burial, could significantly reduce the atmosphere’s carbon levels and address climate change more effectively than traditional methods.
A new way to store carbon captured from the atmosphere developed by researchers from The University of Texas at Austin works much faster than current methods without the harmful chemical accelerants they require.
In new research published today (July 8) in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, the team developed a technique for ultrafast formation of carbon dioxide hydrates. These unique ice-like materials can bury carbon dioxide in the ocean, preventing it from being released into the atmosphere.
Revolutionary Carbon Storage Technique
“We’re staring at a huge challenge — finding a way to safely remove gigatons of carbon from our atmosphere — and hydrates offer a universal solution for carbon storage. For them to be a major piece of the carbon storage pie, we need the technology to grow them rapidly and at scale,” said Vaibhav Bahadur, a professor in the Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering who led the research. “We’ve shown that we can quickly grow hydrates without using any chemicals that offset the environmental benefits of carbon capture.”
Carbon dioxide is the most common greenhouse gas and a major driver of climate change. Carbon capture and sequestration takes carbon out of the atmosphere and stores it permanently. And it is seen as a critical aspect of decarbonizing our planet.
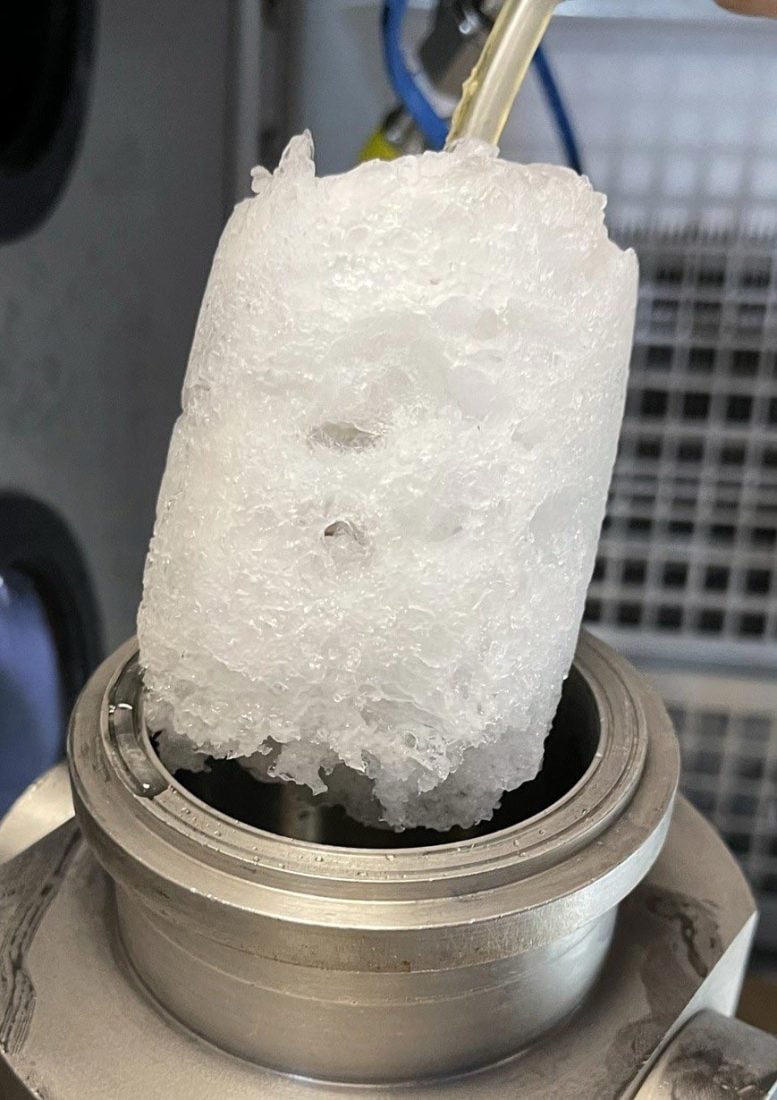

Carbon-capturing hydrates created in Vaibhav Bahadur’s lab. Credit: The University of Texas at Austin
Addressing Challenges in Current Carbon Storage Methods
Today, the most common carbon storage method involves injecting carbon dioxide into underground reservoirs. This technique has the dual benefits of trapping carbon and also increasing oil production.
However, this technique faces significant issues, including carbon dioxide leakage and migration, groundwater contamination, and seismic risks associated with injection. Many parts of the world also lack suitable geologic features for reservoir injection.
Breakthrough in Hydrate Formation for Carbon Storage
Hydrates represent a “plan B” for gigascale carbon storage, Bahadur said, but they could become “plan A” if some of the main issues can be overcome. Until now, the process of forming these carbon-trapping hydrates has been slow and energy-intensive, holding it back as a large-scale means of carbon storage.
In this new study, the researchers achieved a sixfold increase in the hydrate formation rate compared with previous methods. The speed combined with the chemical-free process make it easier to use these hydrates for mass-scale carbon storage.
Implications and Future Applications
Magnesium represents the “secret sauce” in this research, acting as a catalyst that eliminates the need for chemical promoters. This is aided by high flow rate bubbling of CO2 in a specific reactor configuration. This technology works well with seawater, which makes it easier to implement because it doesn’t rely on complex desalination processes to create fresh water.
“Hydrates are attractive carbon storage options since the seabed offers stable thermodynamic conditions, which protects them from decomposing,” Bahadur said. “We are essentially making carbon storage available to every country on the planet that has a coastline; this makes storage more accessible and feasible on a global scale and brings us closer to achieving a sustainable future.”
The implications of this breakthrough extend beyond carbon sequestration. Ultrafast formation of hydrates has potential applications in desalination, gas separation, and gas storage, offering a versatile solution for various industries.
The researchers and UT have filed for a pair of patents related to the technology, and the team is considering a startup to commercialize it.
Reference: “Ultrafast Formation of Carbon Dioxide Hydrate Foam for Carbon Sequestration” by Awan Bhati, Mark Hamalian, Palash V. Acharya and Vaibhav Bahadur, 8 July 2024, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.4c03809